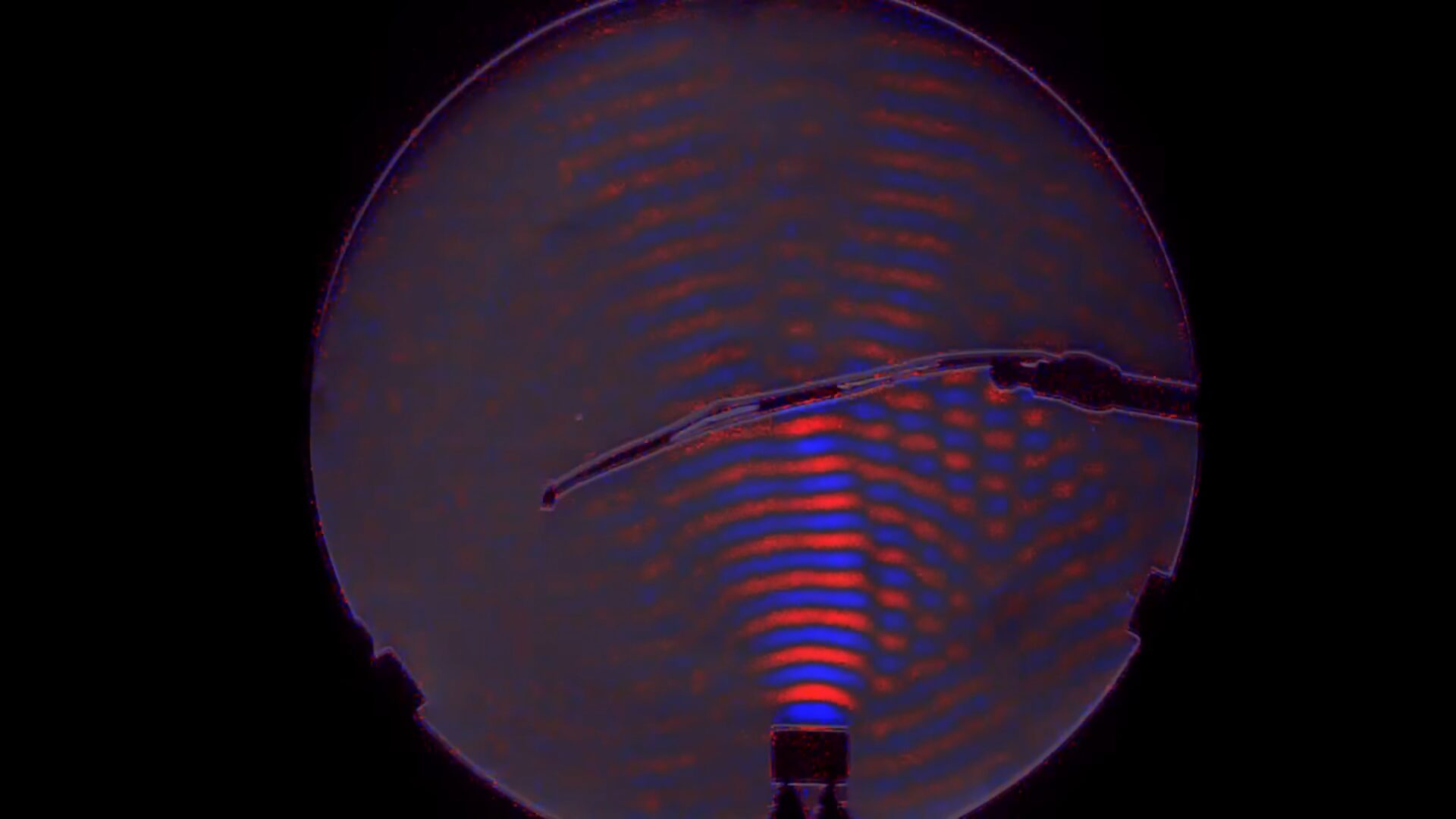
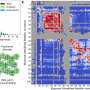
A recent study led by the University of Bayreuth highlights significant challenges in using artificial intelligence (AI) for predicting the properties of new, high-performance materials. Published in the journal Advanced Materials, the research identifies crystallographic disorder as a critical factor causing substantial errors in computer simulations.
The findings reveal that traditional AI methods often struggle with the complex nature of material properties, particularly when dealing with disordered crystalline structures. Such limitations can hinder advancements in various fields, including electronics, energy storage, and materials science, where precise material characteristics are essential.
To address these challenges, the researchers have developed a set of tools aimed at improving the accuracy of AI predictions. They emphasize that enhancing the model’s ability to account for crystallographic disorder could lead to more reliable predictions, opening new avenues for material innovation.
Implications for Material Science
The implications of this research are significant. High-performance materials are vital for numerous applications, from creating more efficient batteries to developing cutting-edge electronics. Errors in predicting their properties can result in wasted resources and delayed advancements. By refining AI techniques, scientists hope to streamline the discovery process for new materials, thus accelerating progress in these critical areas.
The collaborative nature of this international study underscores the importance of shared knowledge in tackling complex scientific problems. Researchers from multiple institutions contributed to the findings, showcasing the collective effort needed to overcome the limitations currently faced in material prediction.
In conclusion, the work from the University of Bayreuth not only sheds light on the limitations of existing AI models but also provides practical solutions to enhance their effectiveness. As the demand for high-performance materials continues to grow, these advancements could play a crucial role in future innovations, making the research a noteworthy step forward in the field of material science.