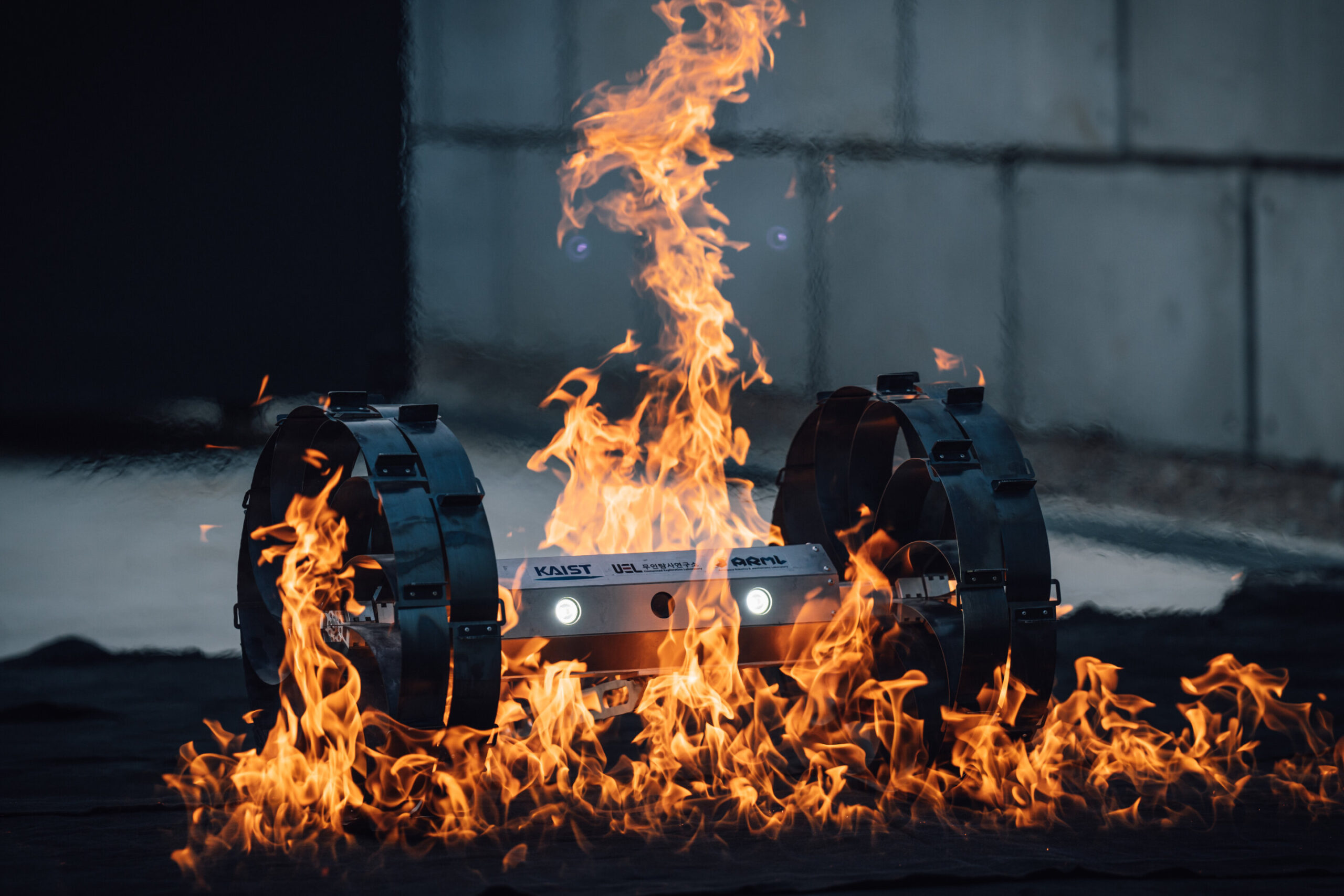
Researchers from South Korea have developed an innovative rover prototype designed to explore the Moon’s uncharted caves, formed by ancient volcanic activity. These lunar caves could serve as critical habitats for future human colonization, providing protection against cosmic radiation and extreme temperatures. The new rover features a unique wheel design that enables it to traverse challenging terrains, making it a significant advancement in lunar exploration technology.
The rover’s wheels are crafted from flexible metal strips arranged in a helix-like pattern. This design allows the wheels to expand and contract, enhancing the rover’s adaptability to different environments. According to a recent study published in the journal Science Robotics, the rover successfully navigated obstacles measuring up to 200 millimeters (approximately 7.8 inches) in height. It demonstrated stable mobility on rocky surfaces and lunar soil simulant, as well as resilience to drop impacts simulating a fall from a height of 100 meters (around 328 feet) under lunar gravity.
The ability to adjust its diameter from nine inches to 19.6 inches allows the rover to distribute weight more evenly, making it capable of negotiating uneven cave landscapes. Unlike other robots that utilize hinges or origami-inspired folds, this rover’s wheel design minimizes vulnerabilities associated with lunar surface hazards. The team conducted extensive tests, including dropping the rover from a height and exposing it to extreme temperatures, to validate the robustness of the wheels.
Future lunar missions could deploy a larger rover equipped with several smaller rovers featuring these innovative wheels. The deployment strategy would involve the larger rover dropping the smaller units at the entrance of a lunar pit leading to a cave. The study emphasizes that the large diameter of the deployable wheels will increase the ground contact area, enhancing traction on uneven surfaces and thick dust.
The researchers noted, “This capability would allow the explorers to navigate challenging pit entrance terrain safely.” The smaller rovers would benefit from the wheels’ elasticity and impact-absorbing qualities, making them well-suited for the demanding conditions of lunar exploration.
The findings highlight the potential of this technology, combining adaptability, durability, and operational efficiency. The innovative wheel design could significantly improve mission outcomes in the unpredictable environments of the Moon. As interest in lunar exploration grows, advancements like these pave the way for future scientific discoveries and the potential for human settlement on our celestial neighbor.