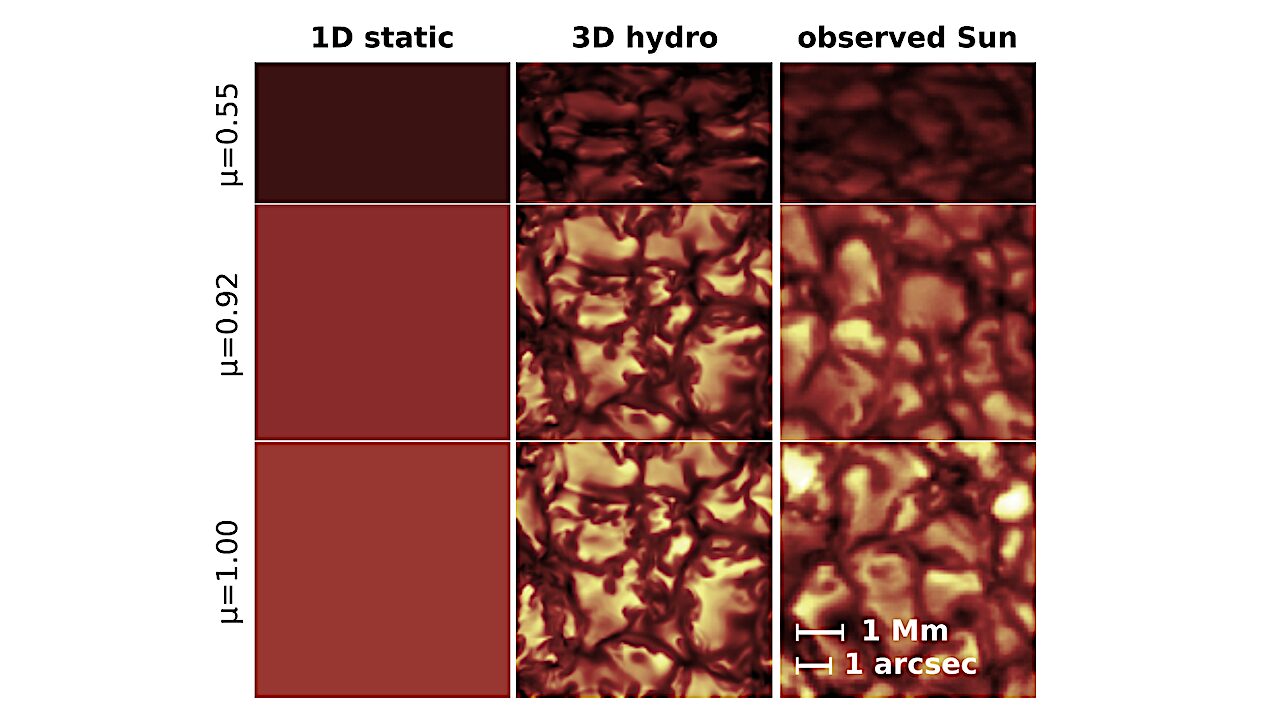
The United States may find a solution to its critical shortage of rare earth elements through the extraction of valuable materials from coal tailings. These byproducts, often discarded from coal mining operations, contain significant amounts of rare earth elements essential for modern technology, including electronics, batteries, and catalysts used in chemical processes.
Understanding Rare Earth Elements
Rare earth elements (REEs) are a group of 17 minerals that play a vital role in various industries. They are crucial for producing high-strength magnets, electronic devices, and components used in renewable energy technologies. Despite their name, these elements are relatively abundant in the Earth’s crust. The challenge lies in their extraction and refinement, processes that have been dominated by China since the 1980s.
The U.S. has struggled to maintain competitiveness in this vital market, with China controlling approximately 60% of global production. As demand for REEs continues to rise, the U.S. government is exploring alternative sources to reduce dependency on foreign supply chains.
Coal Tailings as a Resource
Coal tailings, the waste left over after coal is extracted, are emerging as a promising resource. According to a study from the U.S. Department of Energy, these tailings can contain substantial concentrations of rare earth elements. The potential for recovery from these materials is drawing attention as a means to bolster U.S. supply.
The Environmental Protection Agency has also acknowledged the opportunity presented by coal tailings. The agency is considering regulatory frameworks to facilitate the extraction of REEs while ensuring environmental protections. This initiative could lead to new jobs in the mining sector and contribute to the circular economy by repurposing waste materials.
Recent estimates suggest that the U.S. coal industry produces around 200 million tons of tailings annually. If a fraction of these materials can be processed for rare earth extraction, it could significantly enhance the domestic supply.
Challenges Ahead
Despite the promising prospects, several challenges remain. The extraction process is complex and requires advanced technology to be economically viable. Environmental concerns also persist regarding the potential impacts of mining activities on local ecosystems. Collaboration among government agencies, industry stakeholders, and environmental groups will be essential to address these issues.
In addition, securing the necessary investments to develop infrastructure for processing coal tailings will be crucial. The U.S. government has signaled its commitment to supporting research and development in this field, aiming to create a robust supply chain for rare earth elements independent of foreign sources.
The race for dominance in the rare earth market is intensifying. As the U.S. seeks to regain its footing, leveraging coal tailings could represent a significant step toward achieving energy independence and technological advancement. The outcome of this initiative could reshape the landscape of the rare earth element industry and enhance the U.S. position in global markets.
In summary, the exploration of coal tailings as a source for rare earth elements not only addresses a pressing economic need but also opens up avenues for sustainable resource management. As the U.S. continues to innovate, the potential for a greener and more self-sufficient future remains on the horizon.