Recent advancements in machine learning have enabled researchers to accurately predict individual responses to antidepressants while effectively separating the effects of the medication from placebo responses. This significant development, spearheaded by a team from the University of California, San Diego, addresses a longstanding challenge in treating depression, a condition that impacts approximately 4% of the global population.
Depression is a prevalent mental health issue characterized by a persistent low mood, changes in sleep and eating habits, diminished motivation, and negative thought patterns. Current treatment methods often yield varying results among patients, making it difficult for healthcare providers to determine the most effective course of action. The new machine learning model offers a promising solution by analyzing patient data to tailor antidepressant prescriptions.
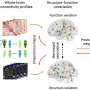
The research team utilized data from a clinical trial involving over 400 participants diagnosed with major depressive disorder. By examining baseline characteristics, such as genetic profiles, demographic information, and clinical histories, the model identified patterns that predict how individuals would respond to specific antidepressants. This approach not only enhances treatment efficacy but could also minimize the time and resources spent on trial-and-error prescribing.
One of the key advantages of this machine learning model is its ability to disentangle the complex interplay between drug effects and placebo responses. This is particularly crucial, given that placebo effects can significantly influence treatment outcomes in psychiatric disorders. The findings suggest that by understanding these dynamics, clinicians can make more informed decisions about prescribing medications.
According to the researchers, this breakthrough could lead to more personalized treatment plans, ensuring that patients receive medications that are more likely to be effective for their specific profiles. As mental health continues to gain recognition as a critical aspect of overall well-being, advancements such as these represent a step forward in addressing the challenges associated with depression treatment.
The implications of this research extend beyond individual treatment. By improving the predictability of antidepressant responses, healthcare systems may enhance the efficiency of mental health care delivery. The potential reduction in trial-and-error prescribing could lead to lower healthcare costs, ultimately benefiting both patients and providers.
As this innovative approach gains traction, further studies will be needed to validate the model’s predictions in larger and more diverse populations. The research team emphasizes the importance of continued collaboration among scientists, clinicians, and data analysts to refine these predictive tools.
In conclusion, the integration of machine learning into the treatment of depression marks a pivotal moment in mental health care. By harnessing the power of technology, researchers are paving the way for more effective and personalized treatment options, ultimately improving the quality of life for millions affected by depression worldwide.