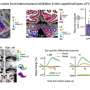
A new advanced footprint tracking system has identified small mammals with an impressive accuracy rate of up to 96%, offering a promising tool for conservation efforts. This technology, developed by scientists at the University of Washington, addresses the growing concern regarding small mammal extinction, a crisis that poses significant threats to global biodiversity.
While larger animals like lions and pandas often capture headlines, the decline of small mammals is equally alarming. These creatures serve as vital indicators of environmental health. Their disappearance could signal broader ecological issues that may affect various ecosystems. Despite their importance, monitoring these small mammals has been challenging due to their similar appearances and diverse ecological roles.
Advancements in Monitoring Technology
The newly implemented tracking system utilizes sophisticated algorithms capable of analyzing footprints, which can often be the only evidence of small mammal presence in an area. Traditional methods of observation and trapping are often inefficient and invasive, leading to skewed population estimates. The researchers’ approach allows for non-invasive data collection, ensuring that animals remain undisturbed in their natural habitats.
According to the study published in Nature Communications, the footprint tracker not only enhances accuracy but also broadens the scope of species that can be monitored. This advancement is particularly relevant as many small mammal species remain under-researched and poorly understood.
Implications for Biodiversity Conservation
The implications of this technology extend beyond mere identification. Conservation scientists believe that accurately monitoring small mammal populations can lead to better resource allocation and targeted conservation strategies. The data collected could help identify critical habitats that require protection and inform policy decisions regarding land use and wildlife management.
The pressing need for effective conservation tools is underscored by the alarming rates of extinction among small mammals globally. Factors such as habitat loss, climate change, and urbanization contribute to their decline. By employing the footprint tracking technology, researchers hope to gain insights that could reverse these trends.
This innovative method marks a significant step forward in wildlife research and conservation. As the effects of environmental change become increasingly evident, tools that enable precise monitoring will be essential in the fight against biodiversity loss. The success of the footprint tracker could inspire similar technologies tailored to other elusive species, further supporting global conservation efforts.
In conclusion, the introduction of accurate footprint tracking technology demonstrates a crucial advancement in understanding and preserving small mammal populations. With a growing crisis in biodiversity, such innovations are vital for ensuring a balanced ecosystem and protecting the critical roles that small mammals play within it.