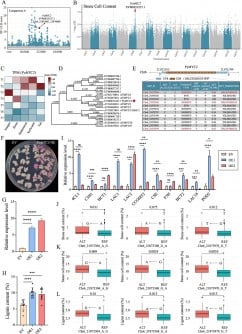
Researchers have developed an innovative organic molecule that significantly enhances energy storage capabilities, storing twice the energy compared to traditional materials. This breakthrough could have profound implications for various applications, including renewable energy systems and electric vehicles.
The study, published in ACS Publications, details that the new organic molecule maintains an impressive 99% capacity retention after nearly 200 cycles of charging and discharging. This level of efficiency is critical for the advancement of energy storage technologies, which are essential for the transition to more sustainable energy sources.
Potential Applications and Impact
The implications of this discovery extend beyond mere energy storage. By improving the efficiency and longevity of energy systems, this organic molecule could facilitate the integration of renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind, into the grid. This is particularly crucial as nations strive to reduce reliance on fossil fuels and combat climate change.
Furthermore, the enhanced energy storage capabilities can significantly benefit electric vehicles. With longer-lasting batteries, manufacturers could produce vehicles that require less frequent charging, addressing one of the primary concerns of potential electric vehicle users.
The research team, comprised of experts in materials science and chemistry, emphasizes that the potential applications for this molecule are vast. As energy demands continue to rise globally, finding solutions that allow for more efficient energy storage will be paramount.
Research Methodology and Future Directions
The team employed a combination of advanced synthesis techniques and rigorous testing protocols to develop and analyze the organic molecule. They focused on optimizing the molecular structure to achieve the desired energy storage characteristics while ensuring durability over multiple cycles. This meticulous approach resulted in a compound that not only stores energy effectively but also resists degradation, a common issue in traditional battery materials.
Looking ahead, the researchers plan to explore further enhancements to the molecule’s performance. They aim to investigate variations that could lead to even greater energy storage capacities and improved cycle life. This ongoing research is vital as the demand for efficient energy storage solutions continues to grow.
In conclusion, the development of this new organic molecule marks a significant step forward in energy storage technology. With its ability to store double the energy and retain an impressive capacity over numerous cycles, it holds the potential to transform how we harness and utilize energy in the future.