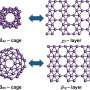
Scientists have established a unified design principle for boron nanostructures, marking a significant advancement in materials science. This development allows for the systematic design of complex boron-based structures, expanding the potential applications in nanotechnology and electronics.
Boron, positioned next to carbon in the periodic table, exhibits a remarkable ability to form intricate bond networks. Unlike carbon, which typically bonds with two or three neighboring atoms, boron can share electrons among multiple atoms. This unique characteristic results in a wide range of nanostructures, including boron fullerenes, which are hollow, cage-like molecules, and borophenes, ultra-thin sheets of boron atoms arranged in triangular and hexagonal patterns.
Significance of Boron Nanostructures
The newly proposed design principle offers a framework for predicting how boron atoms will interact and assemble into various forms. This advancement is particularly important as researchers continue to explore boron’s potential in creating novel materials that exhibit unique electrical and mechanical properties.
According to a research team led by scientists at the University of California, Berkeley, the ability to design boron nanostructures systematically can lead to breakthroughs in fields such as energy storage, sensing technology, and advanced electronic devices. The team’s findings were published in a study in November 2023, highlighting the versatility of boron as a material.
Boron’s diverse bonding capabilities allow it to form structures that can outperform their carbon counterparts in specific applications. For instance, boron-based materials can exhibit higher thermal stability and can be engineered to have superior electrical conductivity. This makes them ideal candidates for next-generation electronic components and energy solutions.
Potential Applications and Future Research
The implications of this research extend beyond theoretical applications. Industries involved in semiconductor manufacturing and renewable energy are particularly interested in the potential of boron nanostructures. Researchers anticipate that the ability to manipulate boron at the nanoscale could lead to the development of more efficient solar cells and batteries.
As the study progresses, the research team plans to collaborate with industry partners to explore practical applications of these boron nanostructures. The focus will be on translating the theoretical models into real-world materials that can be produced at scale.
In summary, the establishment of a unified design principle for boron nanostructures marks a pivotal moment in the exploration of advanced materials. With ongoing research and collaboration, the future of boron-based technologies looks promising, with the potential to revolutionize various fields, from electronics to energy.