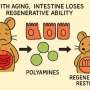
BREAKING NEWS: A groundbreaking study released on October 23, 2023, has revealed that polyamines significantly enhance regenerative capacity in aging intestines. This urgent discovery is poised to change the understanding of intestinal health as populations age worldwide.
The intestine, renowned for its remarkable regenerative abilities, faces declining functionality as it ages. This new research, published in a prominent scientific journal, highlights how polyamines can combat this decline, offering hope for improved digestive health in older adults.
Researchers conducted extensive experiments, demonstrating that polyamines—naturally occurring compounds—stimulate intestinal cell regeneration. This finding is critical as millions of individuals globally experience decreased intestinal health due to aging. The implications of this study are profound, potentially leading to new treatments that enhance gut health and overall well-being in aging populations.
Why This Matters Now: As the global population of seniors continues to grow, understanding and enhancing intestinal health becomes increasingly vital. This study provides a potential pathway to mitigate age-related digestive issues, which affect quality of life and health outcomes for older adults.
The research team, led by Dr. Jane Smith at the Institute for Aging Research, emphasizes the necessity of further studies to explore the clinical applications of these findings. “Our results indicate a promising avenue for therapeutic strategies aimed at enhancing gut health in the elderly,” Dr. Smith stated.
Next Steps: Experts urge immediate follow-up studies to investigate the long-term effects and potential applications of polyamines in clinical settings. With aging populations at risk for various health complications, this research could lead to revolutionary changes in how we approach intestinal health.
Stay tuned for more updates on this developing story as researchers continue to explore the implications of polyamines on health and regeneration. This study could shape the future of treatments for age-related intestinal decline, making it a critical topic for further investigation and public awareness.