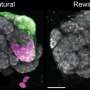
URGENT UPDATE: A groundbreaking study from Stanford University reveals critical insights into how attraction and repulsion shape the neural wiring of fruit flies. Researchers confirm that improper connections among neurons can drastically alter sensory perception, causing something like turpentine to smell akin to a fine chianti.
The implications of this research are enormous, especially considering how sensory processing impacts behavior and decision-making. The study, published on October 15, 2023, emphasizes that the wiring of the brain is not just a matter of structure but also of function—how we perceive the world can pivot on the tiniest neuronal connections.
According to the researchers, the miswiring of neurons involved in the sense of smell can lead to dramatic changes in how an organism interprets its environment. This phenomenon is crucial for understanding not just fruit flies, but potentially broader principles of neural plasticity in other species, including humans.
The study’s lead author stated,
“Our findings underscore the precision required in neural wiring for accurate sensory perception. Even slight misalignments can lead to significant behavioral changes.”
This research offers not just a glimpse into the inner workings of a fruit fly’s mind but raises questions about how similar mechanisms might operate in higher organisms.
Why does this matter RIGHT NOW? As scientists continue to unravel the complexities of the brain, these findings may lead to new approaches in treating sensory processing disorders in humans. The ability to understand and potentially correct miswired neural circuits could aid in developing therapies for conditions such as anosmia, the loss of the sense of smell, and other neurological issues.
Looking ahead, researchers plan to expand their studies by exploring how these findings affect other sensory modalities and different species. The next phase will involve intricate experiments to observe how these neural connections function under various conditions, further illuminating the relationship between attraction, repulsion, and sensory perception.
Stay tuned for more updates as this story develops and as researchers continue to explore the intricate dance of neurons that shapes our understanding of the world. This study not only enlightens the scientific community but also brings us one step closer to understanding the complexities of the brain and its profound impact on behavior.