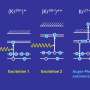
Recent advancements in X-ray technology have led to a significant improvement in photoionization efficiency. Researchers have developed a method that utilizes rapid X-ray pulses to enhance the process by a factor of 100. This breakthrough opens new avenues for scientific exploration and practical applications in various fields.
When an X-ray photon interacts with an atom or ion, it can excite a core electron to a higher energy level. This process creates a brief opportunity—lasting only a few femtoseconds—for a second photon to be absorbed by another core electron. If this occurs, the atom enters a doubly excited state, which has implications for understanding atomic interactions and developing advanced technologies.
The ability to manipulate X-ray pulses with such precision allows for greater control over photoionization. This control is crucial in fields such as quantum computing, materials science, and medical imaging, where enhanced efficiency can lead to more accurate results and faster processes. The implications of this research extend beyond theoretical interests, as the potential applications could transform industries reliant on X-ray technology.
The research was conducted by a team at a leading laboratory, which has been at the forefront of X-ray studies. Their findings have been published in a peer-reviewed journal, highlighting the rigorous methodologies employed and the significance of their results. The study demonstrates not only the feasibility of rapid X-ray pulses but also their advantages over traditional methods.
In summary, the introduction of rapid X-ray pulses represents a vital advancement in photoionization efficiency, with the potential to reshape multiple scientific and industrial sectors. As researchers continue to explore the applications of this technology, the possibilities for innovation remain vast, paving the way for future discoveries that could change how we understand and utilize X-ray interactions.