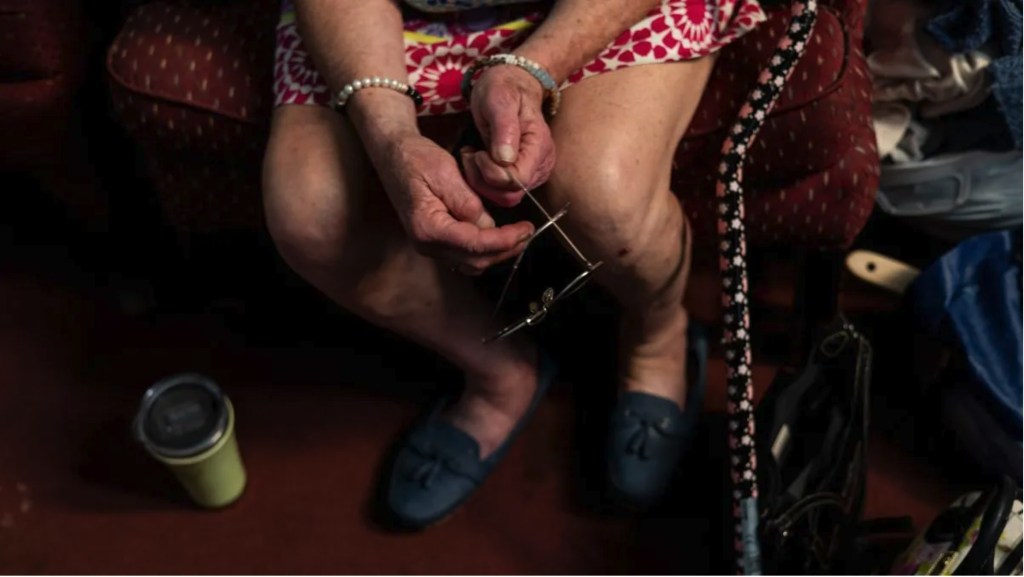
The number of Medicare patients in Maine receiving treatment for opioid addiction through buprenorphine has surged by approximately 70 percent from 2019 to 2023, according to a recent analysis by the Maine Monitor. This trend highlights an alarming aspect of the ongoing opioid crisis, particularly affecting the state’s older population, which has often been overlooked in discussions surrounding addiction and recovery.
The increase in buprenorphine prescriptions indicates a growing recognition of the need for comprehensive addiction treatment among seniors. Buprenorphine is a medication used to treat opioid use disorder by reducing cravings and withdrawal symptoms. The rise in its use among older adults may reflect both increasing awareness of their struggles with addiction and a broader shift towards more accessible treatment options.
Understanding the Context of the Opioid Crisis in Maine
Maine has been significantly impacted by the opioid crisis, which has led to numerous deaths and widespread addiction across various demographics. Traditionally, much of the focus has been on younger populations. However, the data reveals a concerning trend: the state’s older residents are increasingly facing challenges related to opioid misuse.
In recent years, healthcare providers have begun to recognize that addiction does not discriminate by age. Many older adults may have started using opioids for legitimate medical reasons, such as managing chronic pain, but have subsequently developed dependency issues. The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services have been working to enhance access to addiction treatment, which may explain the uptick in buprenorphine usage among Medicare patients.
The findings from the Maine Monitor analysis are crucial for policymakers and healthcare providers. They underscore the need for targeted initiatives that address the unique challenges faced by older adults grappling with substance abuse. Treatment programs must be tailored to meet the specific needs of this demographic, which can include addressing co-occurring health issues and providing support for psychological and social factors related to addiction.
Implications for Healthcare and Policy
The increase in buprenorphine treatment reveals an urgent need for more resources dedicated to addiction treatment for older adults. This demographic often faces stigma and barriers to accessing care, which can hinder their recovery efforts. As the opioid crisis continues to evolve, so too must the strategies employed to combat it.
Healthcare professionals and advocates are calling for more comprehensive education and training for those working with older adults. This includes recognizing the signs of addiction, understanding the complexities of treatment options, and fostering a supportive environment for recovery.
Moreover, policymakers must prioritize funding for programs specifically designed to assist seniors dealing with opioid dependency. Investing in community resources, such as counseling and support groups, can significantly enhance recovery outcomes.
The recent data from Maine serves as a vital reminder that the opioid crisis affects all ages, and it is essential for society to respond with empathy and understanding. As treatment options expand and awareness grows, there is hope for better outcomes for older adults battling addiction.
In conclusion, the substantial rise in buprenorphine treatment among Medicare patients in Maine highlights a critical need for focused attention on older adults in the opioid crisis. Addressing this issue with comprehensive and age-appropriate strategies will be crucial for effective recovery efforts moving forward.